A beginner’s guide to cryptocurrency exchanges
If you want to join the brave new world of cryptocurrencies, your starting point will almost certainly be a cryptocurrency exchange, because that’s where you buy cryptocurrencies. However, their choice can be confusing for a beginner, as there are three main types of exchanges: proprietary abbreviations and terminology. That’s why we’ve outlined the key differences and the pros and cons of each so you can understand what’s important to you.
What is a Cryptocurrency Exchange?
Let’s start with a very simple explanation of what a cryptocurrency exchange is and introduce some of the unique language they use to describe what they do.
A hint of what a cryptocurrency exchange does is verbiage, as a cryptocurrency exchange is a service that allows you to do one of three basic currency exchanges:
- Convert regular money (dollars, euros, yen, etc.) to cryptocurrency
- Exchange cryptocurrency for regular money (dollar, euro, yen, etc.)
- Exchange one cryptocurrency for another
You can compare how a cryptocurrency exchange works to a bureau de change as you see it in an airport. The Forex service provides exchange rates for common currency pairs such as Euro-USD (EUR/USD) or British Pound-Canadian Dollar (GBP/CAD), which show the fluctuating value of one currency against another. You can exchange currency on site for a service fee.
A cryptocurrency exchange offers a very similar (albeit completely online) service that allows you to exchange local currency for a specific cryptocurrency based on similar currency pairs, for example Euro-Bitcoin (EUR/BTC), which shows the current exchange rate of two displays currencies as a currency board.
Cryptocurrency exchanges often describe the exchange rate available for a currency pair as the spot price because the exchange is locally available at that time.
For some newcomers, using the word “price” instead of exchange rate may seem a little strange. We tend to think of goods or services as a price, but not as money.
Although cryptocurrencies act as a new type of money, they are also traded as assets (like stocks), which is why their value is described by the price and also why they fluctuate, as it is very difficult to know what the real price is.
Inputs/outputs and different types of switches
Because we now have two separate financial worlds – fiat and crypto – cryptocurrency exchanges are often described as “ramps up and down” between them.
Just like ramps take you from regular streets to freeways/motorways, cryptocurrency exchanges use traditional fiat-based payment pathways (wire transfers or debit cards) to transfer value to the new payment rails used by blockchain cryptocurrencies.
But if we go back to the three basic functions provided by exchanges, only the first two concern an exchange to or from fiat, which obviously relies on traditional financial services (customers making bank deposits or withdrawals) to stay on the other side. up down.
Any business that uses the banking system in this way must comply with the required rules and regulations, of which there are many. So when you create an account on a cryptocurrency exchange that exchanges fiat, you have to provide a lot of personal information (passport or driver’s license) to comply with these rules known as KYC – Know Your Customer.
This whole process requires a traditional centralized business structure, which is why the most common type of exchange is known as centralized exchange by default.
Centralized Exchange (CEX)
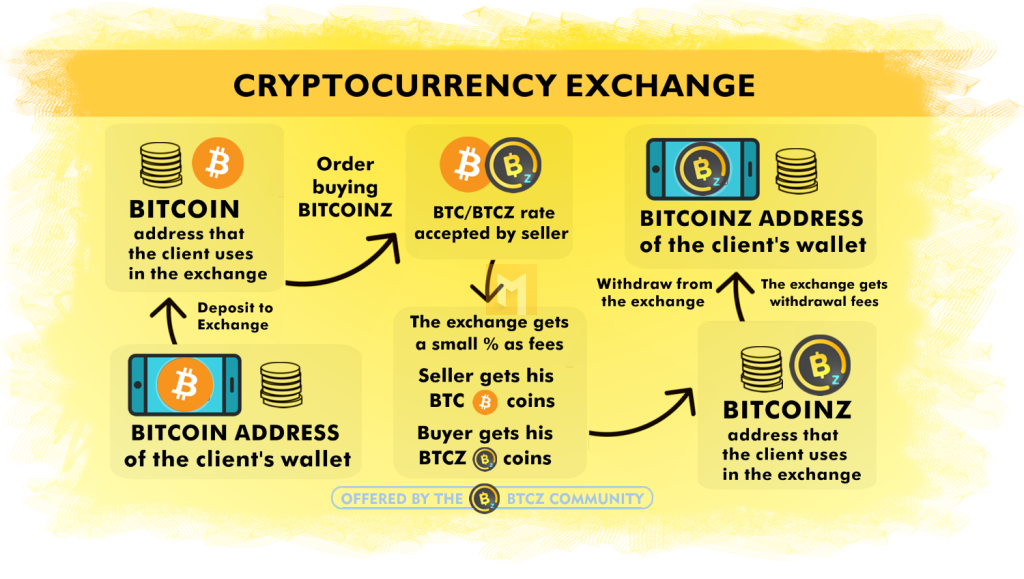
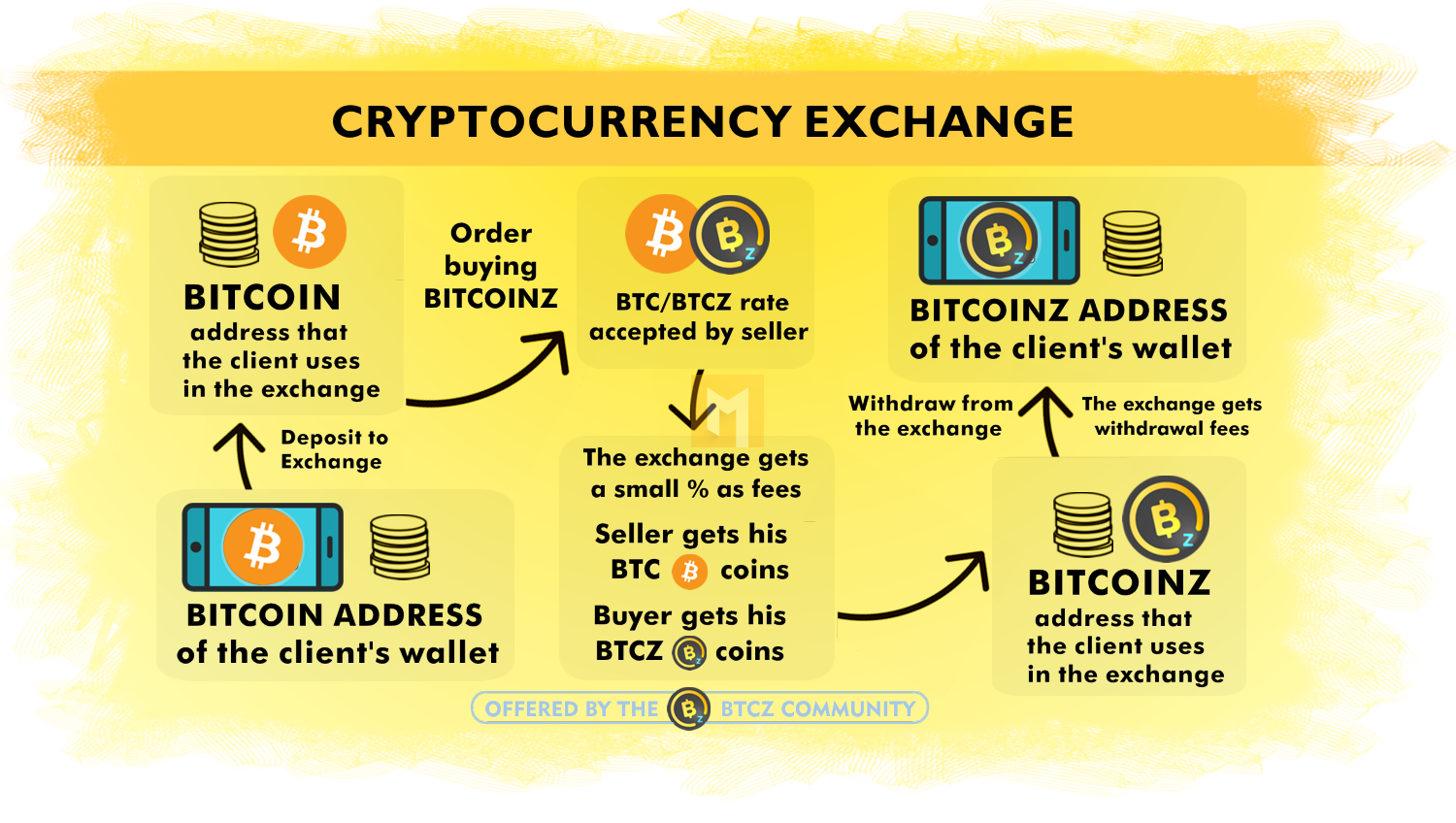
Once you have created an online account on the centralized exchange and passed the KYC, you can deposit and exchange Fiat for cryptocurrencies. The actual exchange process is completely anonymous, in fact you have no idea there is a seller on the other side of the process as the exchange automatically connects buyers and sellers.
Inexperienced exchange users will almost certainly take the bargain price as many exchanges target this group by reducing the buying process to a very simple widget – add card details, spend X, get Y – with the same simplistic approach to sale and exchange of cryptocurrencies.
Of course, not all cryptocurrency exchange users want to buy on the spot, traders want the flexibility to buy/sell/trade based on their perception of where the price is moving. Therefore, there is a simplified widget-like experience for beginners and a completely different view for traders with real-time charts, indicators and trading data. As a beginner, don’t make the mistake of trying your first cryptocurrency trade in the trading view, as it’s a bit like jumping into the cockpit of an F1 after getting your driving license.
How the centralized exchange operates as a business is therefore dictated by the processes/regulations required to handle fiat money, while the service is tailored to the needs of different customer groups. However, this combination requires a very important trade-off that goes against the main value proposition of cryptocurrencies over fiat: being in control.
If you use CEX and buy cryptocurrencies, it will be in your online account, owned by the exchange and not owned by you. Without understanding the concept of custody, this may seem like a reasonable arrangement, similar to how a bank works, but while CEX has similar requirements to a bank, it doesn’t offer the same protection, which is critical as the cryptocurrency world has a significant problem with scams, hacks and business failures.
Therefore, a centralized cryptocurrency exchange is limited to the world of fiat (regular money) and crypto, which determines its design and operation.
Professionals
- It allows you to exchange fiat for cryptocurrencies
- This allows you to sell cryptocurrencies to fiats and withdraw them from your bank
- The user experience is streamlined for newbies and complicated for traders
Versus
- You must provide personal information (KYC).
- The exchange manages your crypto assets, not you
- P2P (peer-to-peer exchange)
A peer-to-peer exchange, sometimes abbreviated to P2P, performs the same basic function as a cryptocurrency exchange, but in a much more centralized way. It removes trading tools and links the buyer to the seller. separate single operation. Think of P2P as person-to-person transactions.
The process is very similar to eBay, where customers deal directly with merchants and P2P Exchange acts as an intermediary, holding funds until the transaction is completed to their satisfaction and mediating any disputes. P2P does not have the automated trading engines of CEX, instead each trader offers a spot price, a choice of payment methods and a trading limit for that price. Sellers have ratings, like eBay, so customers choose them based on a combination of the following factors:
- Price offered
- Choice of payment methods
- How much/little they are willing to trade at that price
- Their rating and the number of previous operations
In the early days of cryptocurrencies, P2P exchanges operated without KYC requirements, making them popular with users who wanted to exchange their Bitcoins, in some cases literally, for physical cash that was exchanged in person once the bitcoin transfer was confirmed.
Given the growing regulation of cryptocurrencies and the potential for money laundering, most P2P exchanges now require some level of KYC, so they have a similar degree of centralization to the CEX approach, but there is still a significant difference.
The convenience of CEX automation/speed has been replaced by a slower but more personalized approach via P2P, giving you a wider range of methods to deposit/withdraw Fiat. Traders/sellers set a price below the spot price. on trades that allow them to make a profit.
Being more than a marketplace to buy/sell cryptocurrencies, P2P platforms are most popular in developing countries – fast growing in Africa and Asia – where commercial transactions are traditionally based on personal interaction and reputation and a bank is less common. account.
Professionals
- One process and more flexibility in terms of payment methods
- Provide a more local service
Versus
- The exchange process is slower
- KYC is generally still required
- Greater chance that something will go wrong