How to manage diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world.
Diabetes affects both children and adults. About 193,000 people under the age of 20 suffer from diabetes in the country.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) notes in its 2017 guidelines that self-management and education are important aspects of diabetes management.
Self-management of diabetes can reduce blood sugar levels, risk of death, and health care costs and weight loss in overweight people.
In this article, we’ll discuss strategies that people with diabetes can use on a daily basis to improve their health.
Self control
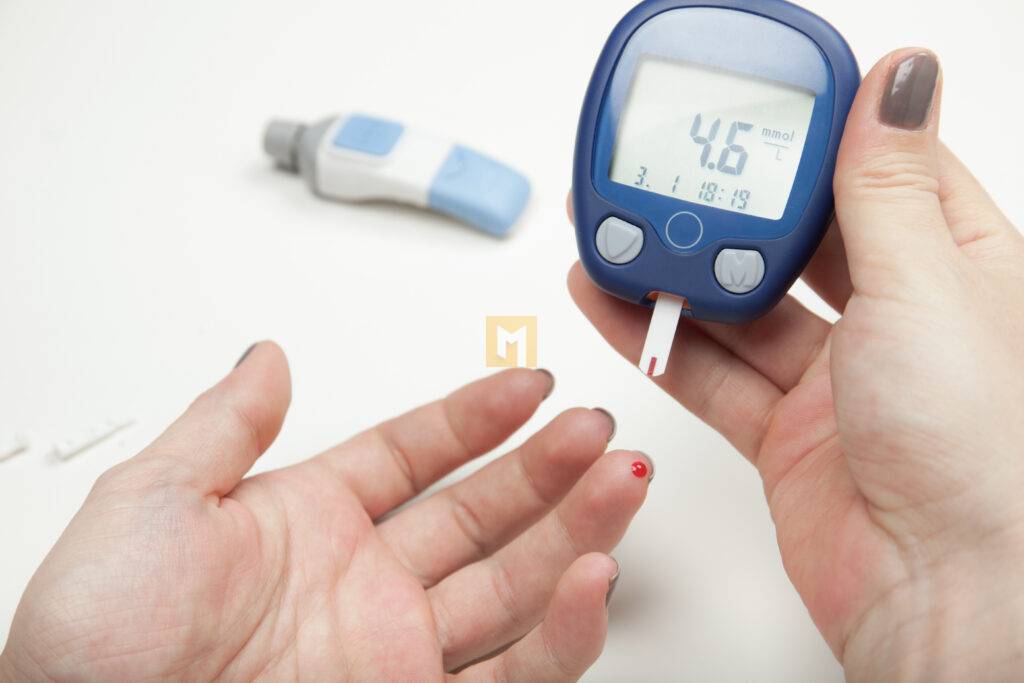
Glycated hemoglobin and blood glucose levels are two important indicators for diabetes control. Measuring glycated hemoglobin requires a blood test in the doctor’s office, but blood sugar can be measured at home.
Doctors advise people using insulin to monitor their blood sugar. The exact frequency of these tests varies from person to person, but doctors generally recommend monitoring levels before and after meals, before bed, and before exercise.
Diabetics who do not take insulin should check their blood sugar. Self-monitoring can provide information about the effects of changes in diet, physical activity, and medications on blood sugar levels.
With a glucometer, you can measure your blood sugar at any time.
There are also continuous glucose meters that provide real-time blood sugar information. They automatically measure the level every 5 minutes using a small sensor inserted under the skin.
When used correctly, this type of technology can improve health outcomes.
Your healthcare team can use your blood glucose readings at home to adjust medication and nutrition plans and for self-monitoring.
Maintain a healthy weight
For people with diabetes or pre-diabetes, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is important. When doctors closely monitor weight loss progress, a person is more likely to achieve their goals.
Research shows that in overweight people, moderate and sustained weight loss can help manage type 2 diabetes and slow the progression of pre-diabetes.
They also note that dietary modification can reduce glycated hemoglobin levels by 0.3 to 2% in adults with type 2 diabetes. Nutritional therapy can also improve quality of life.
To facilitate these lifestyle changes, the ADA recommends consulting with a registered dietitian experienced in diabetes and weight management.
Eat well
Sticking to an eating plan can be one of the most challenging aspects of diabetes self-management. It may help to create a plan with a registered dietitian who is familiar with diabetes nutrition.
Diabetes is a progressive disease, which means it can get worse over time. The ADA recommends using a combination of medication and nutritional therapy to help you reach your blood sugar goals.
Meal planning relies on portion control and healthy food choices. The Diabetic Plaque Method is a tool designed to help people manage their calorie and carbohydrate intake.
This involves mentally dividing the board into three parts. Half the plate should be non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter grains and starches, and one-quarter protein.
Regular exercise
Studies have shown that exercise can help control blood sugar, reduce heart disease risk factors, lose weight and improve health.
Researchers after one study found that participating in a structured exercise program for at least eight weeks reduced glycosylated hemoglobin levels in participants with type 1 diabetes by an average of 0.66%.
The ADA recommends exercising for at least 10 minutes per session and at least 30 minutes total on most days of the week.
If a person exercises every day, or if no more than 2 days pass between exercises, it can help reduce insulin resistance.
A member of the diabetes care team can help develop and coordinate a safe and effective exercise program.
Along with regular exercise, it’s important to avoid sitting for long periods of time. Breaking up your sedentary time into 30-minute intervals can help control blood sugar.
Do not smoke
The ADA recommends that people with prediabetes or diabetes avoid tobacco products, including e-cigarettes.
Diabetics who smoke have more cardiovascular disease, premature death, diabetes complications, and poorer blood sugar control than nonsmokers.
Take medicine regularly
Anasrama is a medical term for not taking medicine as prescribed.
If people with diabetes do not take their medications as recommended by their doctor, it may be for the following reasons:
- Low success rate in achieving clinical goals
- Complications grew
- It increases the risk of premature death
- Increase in overall health costs
A number of issues can contribute to medication adherence. Some may be related to psychological, demographic and social factors. Some of the main factors include treatment costs and health care providers and health system issues.
People with better support networks are more likely to take their medications as prescribed.
Doubts about the seriousness of diabetes and the effectiveness of treatments can discourage people from taking medication, which can lead to complications.
Anemia is more common in chronic diseases with vague symptoms.
The quality of the patient-physician relationship is often an important factor in compliance. It is important for doctors to explain why patients are not following their treatment plan.
Likewise, it is important to discuss any concerns about diabetes treatment with your doctor. Your doctor can adjust your plan to make sure you reach your goals and avoid complications.
Researchers estimate that the total cost of monitoring diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol in the United States in 2010 was $105.8 billion.
Conclusion
There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed at home. This generally includes the following dietary and medicinal regimens.
Quitting smoking is important for good results and there are many programs available.
People with diabetes or pre-diabetes should also be physically active and maintain a healthy weight. Your diabetes care team can help you create and coordinate your exercise program.
Blood glucose meters and continuous blood glucose monitors help people track their progress and see the effectiveness of their management techniques.