How to recognize the symptoms of diabetes
Diabetes limits the body’s ability to control blood sugar or sugar levels. Early recognition of symptoms can help lead to faster diagnosis and prevent complications.
Type 2 is more common.
Both prevent the body from producing and using the hormone insulin. Insulin helps the body regulate blood sugar and ensure it stays at a healthy level.
According to the American Diabetes Association, 26.8 million people in the United States were diagnosed with diabetes in 2018, including about 1.6 million people with type 1 diabetes.
Meanwhile, they estimate that an additional 7.3 million people were undiagnosed with diabetes that year. And in 2015, according to him, about 88 million people were diagnosed with prediabetes – high blood sugar, which indicates that a person may develop diabetes.
Being able to recognize the early signs of diabetes can help one know when to see a doctor.
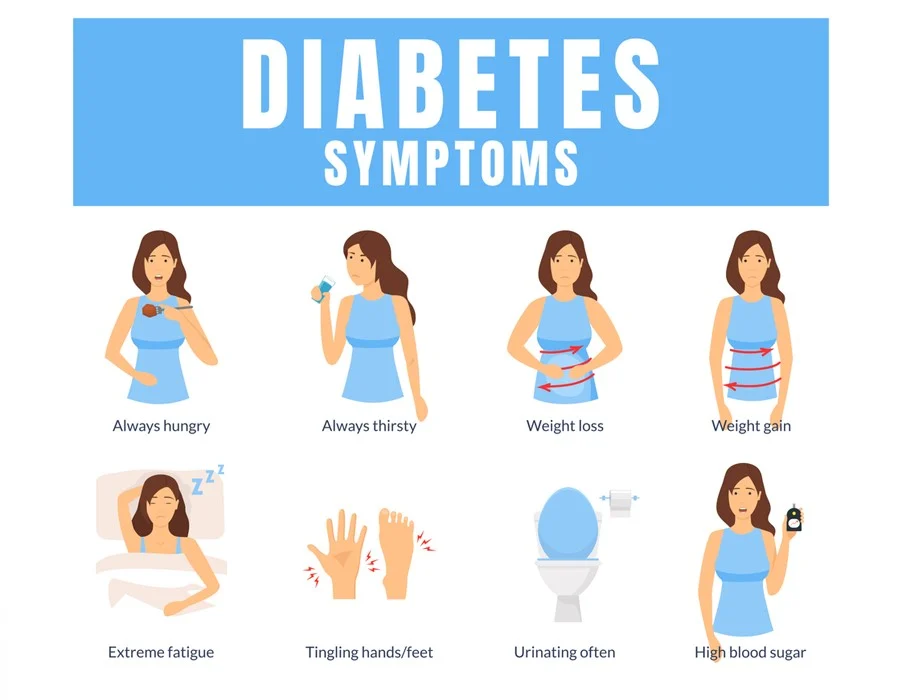
Signs and symbols
Common signs and symptoms of both types of diabetes include:
- get tired
- Feeling hungry during or shortly after a meal
- Discount if you eat more
- Great thirst
- Frequent urination
- Vision is dim
- Cuts and wounds heal slowly
- Numbness, pain or swelling in the hands or feet
- Acanthosis nigricans, a condition that can change the color and texture of the scalp, neck, throat and other areas, can be velvety.
It should be noted that factors such as age and general health can affect how a person experiences these symptoms.
Type 1 diabetes in newborns and infants
Caregivers may notice this.
- get tired
- very hungry
- Unexpected weight loss
- Perspective changes
- A yeast infection, which can appear as a diaper rash
- Breathe
Abnormal behavior such as irritability, restlessness or mood swings
Type 1 diabetes in adults
This condition usually occurs in childhood, but it can occur at any age. You should see a doctor if:
- Unexpected weight loss
- Great thirst
- Frequent urination
- Vision is dim
- Common fungal infections
- Cuts and wounds heal slowly
Type 2 diabetes
Most people are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes during routine monitoring. See your doctor for other symptoms or complications.
Complications of diabetes include:
Skin disease or rash
- Sight and vision change
- Numbness, pain, numbness and weakness in the legs and arms
- Poor circulation and leg ulcers
- Thirst or dry mouth
- Breathe
- The seed problem
How to avoid complications
The earlier a patient with diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner treatment can be started to control blood sugar.
This can happen when a person’s treatment plan is not enough to treat diabetes or there are reasons that prevent a person from following their treatment plan.
Without treatment, high blood sugar can lead to the following complications.
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious disease in which ketones accumulate in the body. Ketone bodies are byproducts that occur when the body breaks down fat for energy.
DKA develops within hours and can be fatal. Early signs and symptoms are:
- stuffy
- severe dry mouth
- high blood sugar
- high levels of ketones in the urine
Next may be:
- exhaustion
- dry or red skin
- vomiting or abdominal pain
- difficulty breathing
- difficulty paying attention
- confusion
Fruity scent in your breath
Long-term complications of diabetes
If a person does not receive effective treatment, the following can occur later in life:
- my heart disease
- brain attack
- kidney failure
Decreased vision
Others have chronic diabetic complications that require amputation.
Early treatment of both types of diabetes can help prevent it.
Cause
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that are responsible for insulin production.
When this happens, the body can no longer produce enough insulin to process and regulate blood sugar.
As a result, people with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin in addition to other treatments and care strategies.
Health experts are still uncertain of the exact cause, but genetics and environmental factors such as viruses may play a role.
Type 2 diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes either don’t produce enough insulin or their bodies don’t use it efficiently.
People with type 2 have too much sugar in their blood, which can lead to symptoms and complications if left untreated.
Type 2 diabetes usually occurs in older people, but it can also occur in younger people.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Other factors also play a role. For example, the condition is more common among blacks and Native Americans than whites.
Type 2 diabetes is also common in people who:
- have obesity
- overcrowded
- They are not physically active or lead a sedentary lifestyle
- excess fat on abdomen
- had gestational diabetes that occurs during pregnancy
- high blood pressure or hypertension
- Over 35 years old
- you have a family history
- Diagnosis and treatment
Doctors usually diagnose diabetes by asking about symptoms and doing blood tests that show high blood sugar.
If there are no symptoms, doctors may do follow-up tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment depends on the type of diabetes. People with type 1 need to take insulin daily by injection or pump.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor may recommend self-care strategies and other ways to control your blood sugar. This may include taking medications containing insulin.
It is important to follow the recommended treatment regimen. Anyone who finds it difficult to do so or experiences side effects should immediately consult a doctor for guidance.
Overview
Finding the early symptoms of diabetes can help you get a timely diagnosis and start treatment right away. This helps prevent complications of diabetes that can be very serious.
People who think they may have diabetes should contact their doctor.