Blockchains
What is Proof of Work in Blockchain?
What is Proof of Work in Blockchain?
The original purpose of cryptocurrencies included decentralization as the most important part. This required a method for confirming transactions without the intervention of financial institutions. The certificate of work was the first answer to this problem.
Proof of work (PoW) is a way to add new transaction blocks to a cryptocurrency blockchain. In this scenario, the task generates a hash (a long string) that matches the target hash value of the current block. This authorizes the cryptominer to add that block to the blockchain and receive rewards.
Because proof-of-work is the consensus technology used by the first cryptocurrency Bitcoin, the cryptocurrency evolved from it (CRYPTO:BTC). It is known for its safety, but it is also known for its inefficiency and negative environmental impact.
You will get a better understanding of coins using proof of work if you understand it. This can also help you decide where to invest your crypto fund. Read on for a full explanation of the certificate of employment.
Definition of the certificate of work
Instead, they rely on a network of participants to validate incoming transactions and add them as new blocks to the chain.
Proof-of-work is a consensus technique that allows network participants – miners – to determine which of them is authorized to do the profitable job of verifying new information. It is profitable because miners are rewarded with new cryptocurrencies for properly validating new information and not cheating the system.
Proof of Work is a software method used by Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications to ensure that blocks are only considered genuine if they cost a certain amount of processing power to produce. It is a decentralized network consensus technology that allows anonymous entities to trust each other.
The word “work” is crucial to proof of work: To keep anyone from playing the system, the method requires miners to compete with each other to be the first to answer random mathematical puzzles. The contest winner is selected to upload the latest batch of data or event to the blockchain. Winning miners will only receive their new bitcoin reward when other network participants confirm that the information added to the chain is correct and authentic.
Why is the work certificate important?
Satoshi Nakamoto founded the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, in 2008. Nakamoto wrote a well-known white paper describing a digital currency based on a proof-of-work protocol that enables secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a centralized authority .
The double-spend problem has been one of the obstacles that prevented the creation of a viable digital currency in the past. Since cryptocurrencies are just data, a technique is needed to prevent users from using the same drives in multiple places before the system can record the transactions.
While it would be difficult to spend the same dollar bill twice, anyone who has copied and pasted a computer file can no doubt imagine how digital money can be spent twice, even ten times or more.
The double-spend problem was overcome with Nakamoto’s consensus technique. Proof-of-work helps avoid double-spending by motivating miners to verify the integrity of new cryptographic transactions before adding them to a distributed ledger called a blockchain.
How the proof-of-work model works
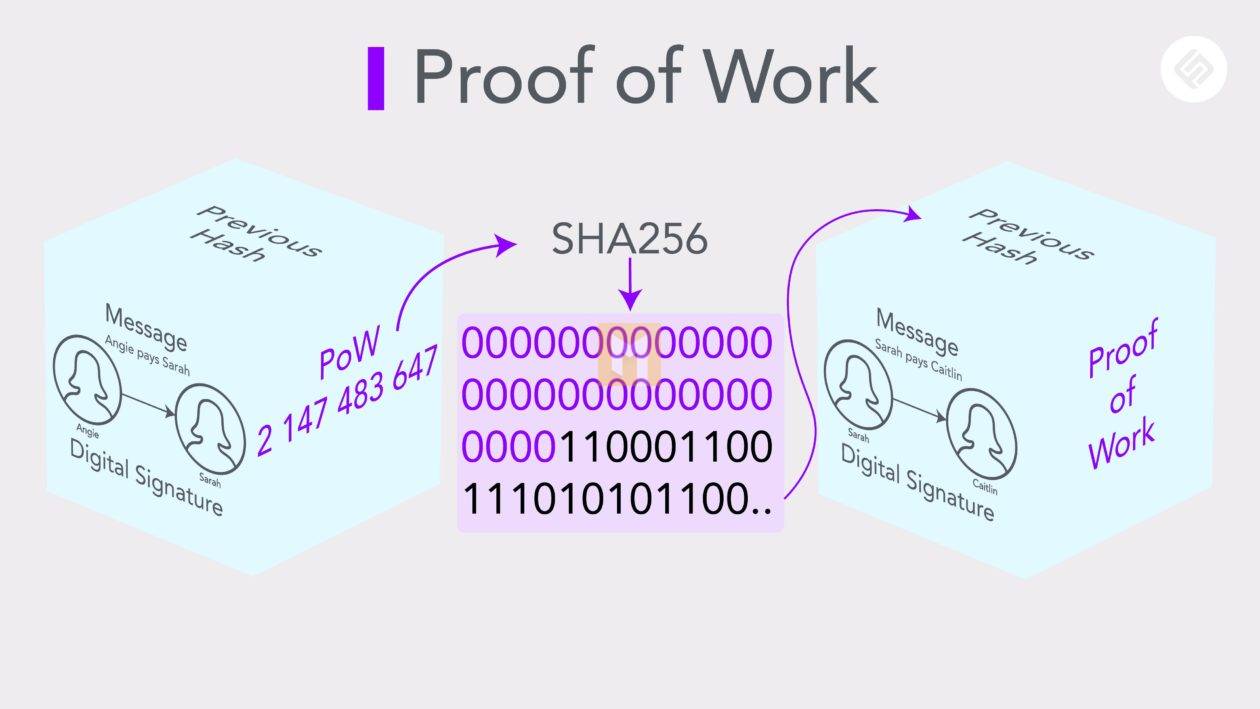
The consensus process used to validate and record bitcoin transactions is the proof-of-work model. Blockchain, a public ledger composed of blocks of transactions, is present in all cryptocurrencies. Each block of proof-of-work cryptocurrency transactions has a unique hash. A cryptominer must generate a target hash value less than or equal to the block hash to validate the block.
Miners do this using mining machines that produce calculations quickly. The goal is to be the first miner to hit the target hash as this miner can upgrade the blockchain and receive cryptocurrency incentives.
Since getting the target hash is difficult, but not verifying it proves that bitcoin works well. The method is complex enough to avoid tampering with transaction records. At the same time, it’s easy for other miners to explore the target hash once they find it.
How Bitcoin uses Proof of Work
When a Bitcoin transaction is made, it goes through a security check and is then compiled into a block that can be mined. The block is then hashed using Bitcoin’s proof-of-work mechanism. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm, which always produces 64-character hashes.
Miners compete for a target hash smaller than the block’s hash. The winner gets the privilege of adding the most recent transaction block to the Bitcoin network. They are also rewarded with Bitcoin in the form of new coins and transaction fees. Bitcoin has a predetermined maximum supply of 21 million coins, though miners are still compensated for their services afterward.
To do this, it adjusts the Bitcoin mining difficulty based on how quickly miners add blocks. Hash calculation becomes more difficult if mining happens too fast. They get easier when the pace is too slow.
Criticism of work certificates
Proof-of-work systems have received a lot of criticism, largely due to their voracious appetite for electricity:
- Energy requirements. According to the New York Times, in 2009 a standard desktop computer and a small amount of electricity could mine one Bitcoin. However, to mine one Bitcoin in 2021, you’d need to consume enough electricity to power a typical American home for nine years.
- Decentralization is one of the most attractive benefits for bitcoin investors. Mining has consolidated into a small number of large companies due to the heavy calculation and energy requirements of work certificates. This could lead to some companies controlling most of the bitcoin business.