Health
What is the average baby weight by month?

What is the average baby weight by month?
Weight is an indicator of proper nutrition and physical development. That is why it is useful to know the average weight of children every month.
First of all, it is important to note that average weight is not “normal” weight. If a child’s weight is in the lower percentile, it doesn’t necessarily mean problems with growth or physical development. Therefore, using a weight chart can help track a child’s growth.
Credible sources from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using the World Health Organization (WHO) weight chart for children under age 2.
This article describes the average monthly weight of a baby since birth. He also finds out what can affect the weight of the child.
Average weight of a child
According to WHO, the average birth weight of a full-term male baby is 7 pounds (lbs) 6 ounces (oz) from reliable sources, or 3.3 kilograms (kg). The average weight of a full-term female is 7 pounds 2 ounces or 3.2 kg, according to reliable sources.
The average birth weight of a baby from 37 to 40 weeks old is 5 pounds 8 ounces and 8 pounds 13 ounces. They weigh from 2.5 to 4 kg.
A birth weight of less than 5 pounds 8 ounces or 2.5 kg is considered a reliable source by birth professionals.
Babies usually lose about 10% of their body weight shortly after birth. This deficiency is mainly due to fluid loss and is usually not a cause for concern. Most children regain their weight within 1 week.
Weight table for children by age
A weight chart can help determine how much weight a baby will lose. For example, if their weight is in the 60th percentile, this means that 40% of children of the same age and sex are overweight, and 60% of those children are underweight.
This does not mean that the child is overweight or underweight. It can simply indicate where the child’s weight falls on the spectrum.
The table below shows the weight of children in the 50th percentile. It’s the average weight. Boys weigh slightly more than girls, so the table is divided by gender.
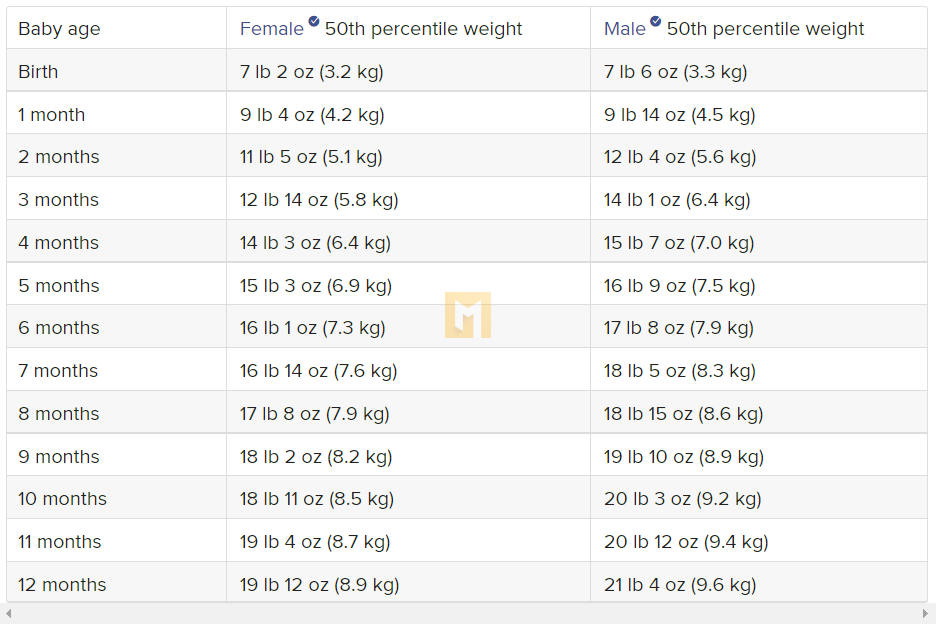
What is the average baby weight by month?
Here’s what to expect
Babies grow and gain the fastest weight in the first 6 months of life. While it can vary, babies typically consume about 4-7 ounces or 113-200 grams (g) per week for the first 4-6 months.
After that, weight gain slows slightly, averaging 3 to 5 ounces (about 85 to 140 grams) per week when babies are 6 to 18 months old.
However, the development model does not follow a clear timeline.
Some children gain weight steadily and stay at or near the same rate for several months. Others lose weight quickly, indicating a growth spurt that can occur at any time. This can result in a new percentage of the baby’s weight.
What Affects a Child’s Weight?
It is important not to focus on weight as the sole indicator of physical performance. Other indicators of this development are the length and girth of the baby’s head.
The three-dimensional scan gives doctors a picture of how the child is growing compared to other children of the same age and gender.
In the meantime, other critical points of development should be mentioned. Several milestone age checklists are available, including one from Pathways.org, which is endorsed by organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Association of Pediatric Nurses.
For those wanting more information about what affects a baby’s weight, several factors may come into play, including:
Sex
Male babies are larger than female babies and generally gain weight a little faster during infancy.
Nutrition
Weight and growth can also depend on whether the child is breastfed or formula fed.
The American Academy of Pediatrics notes that breastfed babies gain weight during the first 6 months and grow faster than formula-fed babies.
However, this percentage may change within the next 6 months. Breastfed babies can gain weight from 6 months to 1 year more slowly than formula-fed babies.
The disease
A child may gain weight slowly due to underlying health problems. For example, children with congenital heart defects may gain weight more slowly than children without the condition.
Health conditions that affect the absorption or digestion of nutrients, such as celiac disease, can cause gradual weight gain.
Premature
Premature babies may grow and gain weight more slowly in the first year than full-term babies.
But many premature babies gain weight quickly and “catch up” after their first birthday.
Compendious
The average birth weight for full-term male babies is 7 pounds 6 ounces or 3.3 kg. The average birth weight for full-term women is 7 pounds 2 ounces or 3.2 kg.
A child’s weight chart can help the health care team monitor the child’s physical development by comparing the child’s weight with the weight of others of the same age and gender.
However, doctors often look at growth rates rather than percentages when assessing a child’s physical growth. Even if the child’s weight is in the bottom percentile, the child will neither be taller nor shorter in length.
Knowing the average monthly weight can help people track a child’s physical growth, but doctors also look for other important parameters, such as length and head circumference.
Health professionals also expect children to often go through other milestones over time. And by taking a thorough medical history, they can rule out diseases or nutritional problems that might prevent a child from gaining enough weight.