Health
Arthritis in the knee: What you need to know
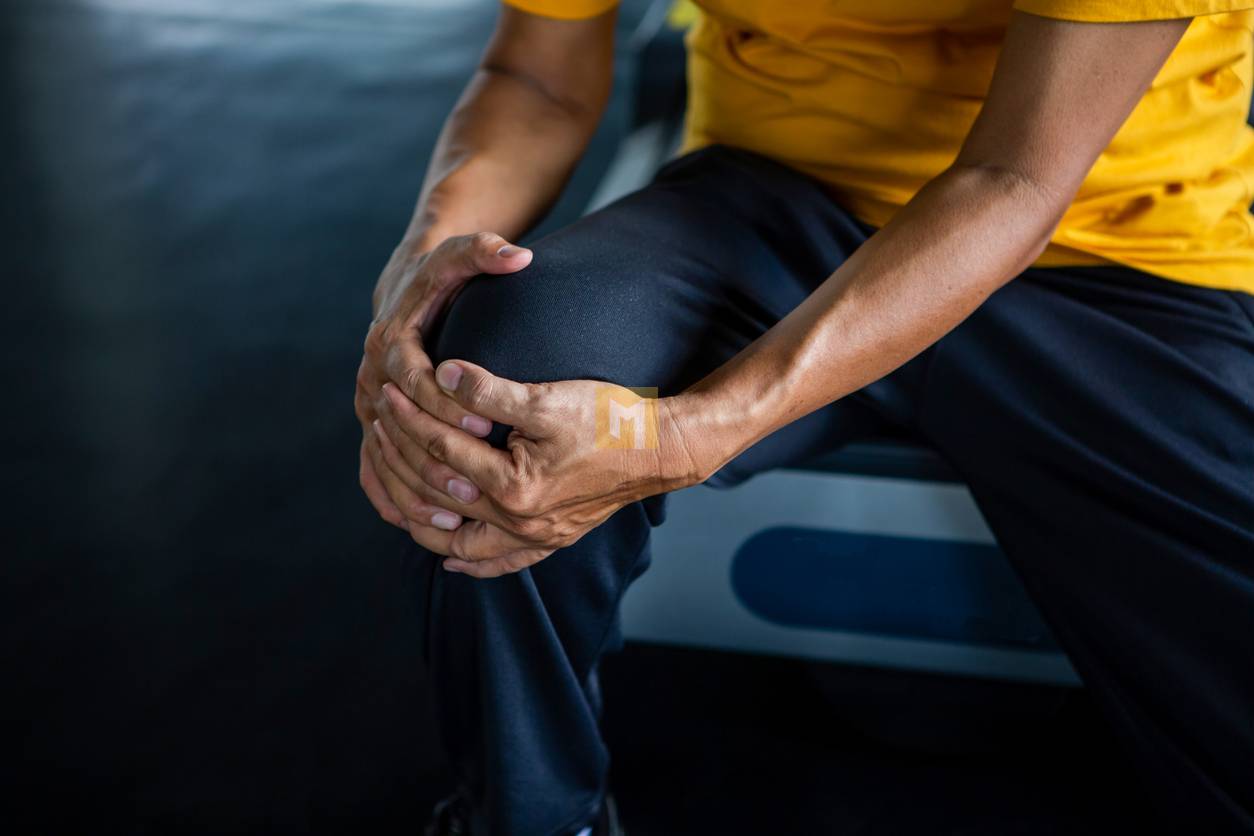
Arthritis in the knee: What you need to know
Walking with knee arthritis can be painful. Swelling, pain, and stiffness in the joints are some of the symptoms that can accompany this condition.
The knee joint is a valve joint, so named because its movement resembles that of a door opening and closing.
Joints consist of three main bones. Where two bones meet, each bone is covered with protective cartilage. Additional cartilage, called the meniscus, provides additional support to the bone.
All of these protective cartilage sheets prevent the bones of your knee from rubbing against each other.
The constant stress and strain on the knee, and the damage it can cause, makes it a common cause of arthritis. There are different types of arthritis, and the type determines the treatment your doctor recommends.
Symbol
Symptoms commonly associated with knee arthritis include:
- Crepitus is a creaking or creaking sound produced by the knee joint during walking.
- Illness that seems to be weather-related and aggravated by rain.
- hardness
- swelling
- Weakness of the knee joint, which can lead to curvature.
Hot, red joints are often signs of arthritis, but can occur with almost any arthritis, depending on the level of inflammation.
The symptoms of knee arthritis usually worsen over time.
Advanced arthritis is characterized by deformity and stiffness of the joints, making movement very difficult. However, severe symptoms of knee osteoarthritis can appear suddenly.
Types
According to the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS), there are over 100 types of arthritis, some of which are common to the knee.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the common form of knee arthritis.
This happens when the protective cartilage covering the bone wears away.
As the cartilage wears away, the bones begin to rub against the knee joint.
This causes bone spurs to appear at the ends of the bones. Bone spurs can be painful and limit a person’s mobility.
Post-traumatic arthritis
Chronic damage to the bone and adjacent joints continues to affect a person and post-traumatic arthritis, a type of arthritis that develops after an injury.
The injury causes excessive wear and tear on the knee joint, leading to osteoarthritis. Painful swelling may occur at the knee joint.
Gouty arthritis
Hemorrhoid is a form of arthritis in which uric acid crystals form in the joints, including the bones. Uric acid is a waste product produced by the breakdown of body tissues.
The crystals look like tiny needles. They cause inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. This means that the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells.
This condition tricks the body into believing that healthy tissues, such as… B. protective cartilage, are harmful. As a result, the immune system breaks down and destroys these tissues.
RA can cause swelling and tenderness of the knee joints.
Reason
The cause of each knee arthritis is different.
Osteoarthritis
Doctors consider OA a “wear and tear” condition because the cartilage wears away when the bone is used. OA usually occurs after the age of 50 because it is a condition of overuse.
Gouty arthritis
Gouty arthritis can have different causes or risk factors. These include:
- age
- Family history of gouty arthritis.
- As a man, you are more attracted to a man
- Obesity, like being overweight, means there is more tissue to break down uric acid.
- Use of certain medications
Jupiter usually starts from the thumb. Kidney stones and lumps under the skin.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes rheumatoid arthritis, but genetics may play a role.
Post-traumatic arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis is a type of OA that occurs as a result of a previous injury to the knee joint, such as cartilage or a tear.
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose knee arthritis through a physical exam, imaging studies, and laboratory tests.
First, the doctor examines the person’s medical history. Next, he examines the knee by looking at it, touching it, and asking for movement if possible.
Doctors look for arthritis symptoms and injuries in the knees and elsewhere because some arthritis often affects other parts of the body.
They also appear where arthritis is located in the body. Some types of arthritis affect only one knee, while others usually affect both knees.
Doctors also recommend imaging studies to check for changes in the knee joints.
Examples include:
- X-ray
- Cat scan
- MRI scan
The latter two scan options help doctors identify soft tissue damage to the patella.
Laboratory tests for rheumatoid factor, an antibody common in rheumatoid arthritis patients, can help confirm the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment and home care
Doctors often treat the early symptoms of arthritis with home remedies to reduce pain and prevent symptoms from getting worse. Over time, people may need stronger drugs or surgery.
Alternative therapy
Many supplements or alternative therapies can also help reduce pain and other symptoms.
Examples:
Acupuncture: Doctors insert thin needles into specific parts of the body.
Children’s neotherapy: This involves soaking the knee joint in a hot mineral spring.
However, there is no evidence that this drug is effective for all people with arthritis.
Some people use transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain relief. This device sends a weak electric current to a part of the skin.
But the American College of Arthritis and the Arthritis Foundation do not recommend this treatment because there is not enough evidence to show that it helps.
Medication
If home and self-care options do not work and the symptoms worsen, the person may need treatment.
Duloxetine (Cymbalta) is an antidepressant that helps with chronic pain.
Capsaicin, which comes from chili peppers, is found in some topical lotions and creams.
Risedronate (Actonel) is a treatment for osteoporosis, but it helps preserve cartilage.
All of these medications can have side effects. Who should talk to their doctor about what is right for them?
Capsaicin ointments and creams can cause redness and pain. People should not use it if they have other diseases.
Surgery
Knee surgery is often the last resort for knee arthritis.
Examples of these processes include:
Arthroscopy: The surgeon inserts a small instrument into the knee to examine the area for possible damage. At the same time, removing the broken bone from the knee or removing the joint can reduce pain. If the meniscus or ligaments around the knee are torn, doctors can repair the area together.
Cartilage transplant: Doctors can transplant cartilage from other parts of the body and transfer it to the knee bone.
Total or partial knee replacement: The surgeon removes the damaged knee joint and replaces it with a metal or plastic joint that is supposed to resemble the real knee joint.
Other causes of knee pain
Arthritis doesn’t just cause knee pain. Some other diseases have similar symptoms.
Examples:
Diseases that affect the whole body, such as lupus, sepsis, acute infections
Inflammation in the area around a joint, such as a tendon
Anyone with knee pain, especially swelling, should see a doctor.