Health
What should my cholesterol level be at my age?

What should my cholesterol level be at my age?
The body produces more cholesterol over time, so doctors recommend that everyone over the age of 20 get their cholesterol checked regularly, preferably every five years.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that approximately 94 million adults in the United States have high cholesterol.
In this article, we explain how doctors measure cholesterol and explain healthy levels at different stages of life. We also research ways to lower cholesterol and maintain healthy levels.
What is cholesterol and how do doctors measure it?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fatty substance that comes in two types: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
If there is too much LDL cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, in the blood, it can build up in the blood vessels and cause fatty deposits called plaques. These plaques can also lead to other problems, such as heart attacks and strokes.
But having more HDL cholesterol (or “good” cholesterol) in your blood can reduce your risk of heart attack or stroke.
Your doctor can measure your HDL, LDL, and total cholesterol levels. The results may suggest that all non-HDL fats may increase the risk of heart disease.
Cholesterol levels and age
Cholesterol levels increase with age. Taking measures to achieve or maintain fitness levels early in life can prevent them from becoming dangerous over time. Years of uncontrolled cholesterol levels can be difficult to treat.
The CDC recommends that people age 20 and older have their cholesterol levels checked every five years or more often if they have other cardiovascular risk factors.
Children have elevated cholesterol levels, and doctors should check cholesterol levels twice before the age of 18.
However, children with risk factors for high cholesterol should be screened more often.
Men tend to have a higher lifetime prevalence than women. Cholesterol levels increase with age in men and women after menopause.
The chart below shows healthy cholesterol levels by age, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
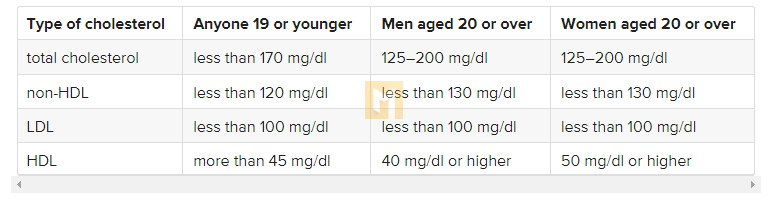
What should my cholesterol level be at my age?
Recommended cholesterol levels
- In addition to aging, changes in cholesterol levels are often due to health and lifestyle factors.
- The healthy and unhealthy categories are described in more detail below.
- Cholesterol levels in adults
- Doctors can classify people’s levels as high or low, borderline or healthy.
Total cholesterol
A total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dl is healthy for an adult.
Doctors consider a reading of 200-239 mg/dl as borderline high and at least 240 mg/dl as high.
LDL cholesterol
Doctors may not be concerned about levels between 100 and 129 mg/dL in people without medical problems, but they may recommend treatment at this point for people with heart disease or risk factors.
If a person’s reading is 130-159 mg/dL, that is the upper limit, and a reading of 160-189 mg/dL is high. A reading of at least 190 mg/dl is meaningful.
HDL cholesterol
Doctors recommend maintaining HDL levels. People with readings below 40 mg/dL may be at risk for heart disease.
If a person’s reading is 41-59 mg/dl, doctors consider this limit to be low. The optimal HDL level is 60 mg/dL or higher.
Cholesterol Levels for Children
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, children should have total cholesterol less than 170 mg/dL.
The upper range is 170-199 mg/dl, with a reading of 200 mg/dl or higher.
The upper range is 110-129 mg/dl, any reading above 130 mg/dl.
Other Factors Affecting Blood Cholesterol
Various health conditions and lifestyle factors can raise cholesterol levels, CDCT sources say. For example, type 2 diabetes raises LDL cholesterol levels, as does familial hypercholesterolemia.
The CDC also says that a diet high in saturated fat and little exercise can raise cholesterol levels.
In addition, he recognizes that the risk increases for a person when their family members have high cholesterol.
How to lower cholesterol
The NIHT recommends these strategies to lower cholesterol levels:
- A diet rich in heart-healthy foods from reliable sources, including plenty of fruit and vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains
- Be more active
- Quit smoking (if applicable)
- Medium weight
- Stress management
The National Institutes of Health recommends consulting a health professional before starting a new exercise program, but generally recommends that a person get at least 30 minutes of exercise per day.
A healthy diet and adequate exercise can reduce high cholesterol in children.
In general, the sooner a person starts making these changes, the better their cholesterol levels will improve, as cholesterol can build up over time.
These risks will increase over time.
Drug therapy for high cholesterol
If high cholesterol cannot be reduced with lifestyle changes alone, your doctor may prescribe medication. The CDC reports that the following medications and supplements may help:
Statins: These drugs prevent the liver from making cholesterol.
Bile acid sequestrants: These drugs reduce the amount of fat your body absorbs from food.
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors: These drugs lower the level of fat in the blood called triglycerides and reduce the amount of cholesterol absorbed from food.
Certain vitamins and supplements: These, like niacin, prevent the liver from lowering HDL and triglyceride levels.
Omega-3 fatty acids: These increase HDL levels and lower triglyceride levels.
When to talk to a doctor
Before the age of 18, the child’s cholesterol level should be checked by a doctor at least twice. If your child has a family history of heart disease, obesity, or certain other health conditions, the doctor may recommend more frequent level checks.
Adults aged 20 and over should have their cholesterol checked by a health care professional every 4-6 years.
Your doctor may recommend treatment if:
- The results showed high or near-high levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol.
- This person is overweight.
Abstract
Cholesterol levels increase with age and cholesterol at any age increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Achieving or maintaining a level of fitness may involve lifestyle changes and, if these are not sufficient, prescription medication.
Doctors should check cholesterol levels in adults every 4-6 years starting at age 20.