Health
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
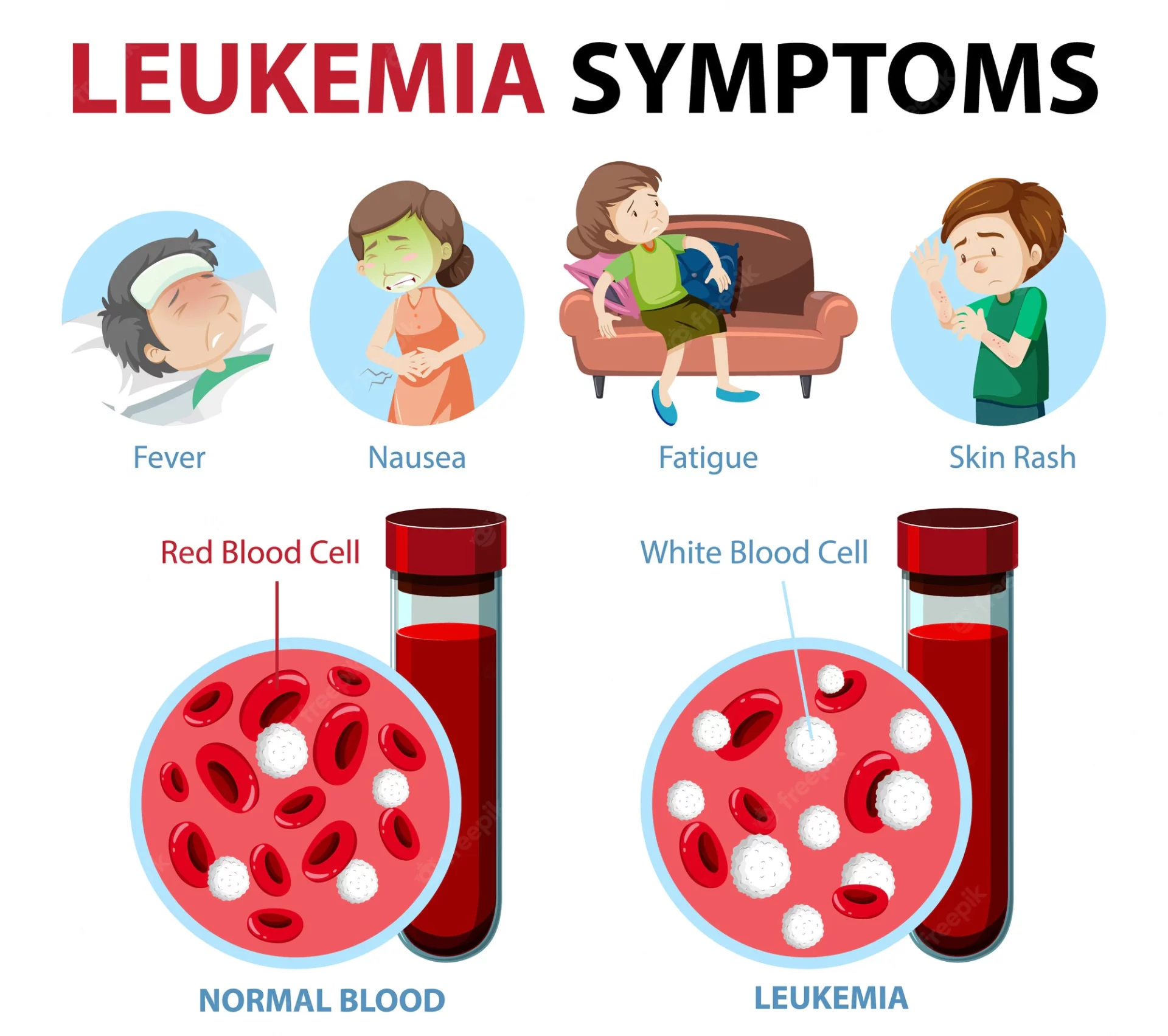
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
Leukemia is a general term for cancer that affects a person’s blood or bone marrow. There are different types of leukemia, but because they affect the blood cells, they have many of the same signs and symptoms.
In this article we will look at the different symptoms of leukemia, why they occur and when you should see a doctor. We will also briefly discuss causes and risk factors, diagnosis and treatment options.
Symptoms of leukemia
Leukemia symptoms can vary depending on a person’s age, the type of leukemia, and the stage of the disease.
Pediatric leukemia
Signs of leukemia in children can be difficult to recognize. Children cannot describe their symptoms as easily as adults.
Common signs and symptoms of leukemia in children include:
- Reduced appetite
- Bleeding from the gums
- Bone pain
- Dizziness
- Bleeds easily
- fragile
- Fever apart from other signs of infection
- Frequent cough
- Recurrent infections or recurring infections that take a long time to clear up
- Joint pain
- Gasping
- rash
- Swollen lymph nodes that can be felt under the armpit, over the shoulder or in the neck
- Fatigue beyond comprehension
- Unexpected weight loss
Many of these symptoms can be similar to other childhood illnesses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus or pneumonia.
Adult characteristics
Symptoms of leukemia in adults range from general discomfort to seizures due to problems with the immune system, the spleen.
A person may experience symptoms such as:
-
Non-specific symptoms
Sometimes a person may experience flu-like symptoms that are not related to leukemia. These symptoms are usually related to the destruction of the body’s blood cells and the increased energy the body needs to fight disease.
Features include:
- Reduced appetite
- hot
- Cold sweat
- Unexpected weight loss
When diagnosing these symptoms, doctors often associate them with leukemia.
-
To shine
As leukemia cells grow, they can begin to accumulate in the spleen and liver. Additional cells can increase the growth of these organs. As a result, you may feel full or dizzy.
-
Bleeding problems
Some types of leukemia can destroy platelets, a type of blood cell that prevents blood from clotting. As a result, you may notice that wounds bleed more easily. You may also have bleeding gums or frequent nosebleeds.
-
Bone or joint pain
Abnormal cells can accumulate near or inside the bone, causing bone or joint pain. This pain can vary from a dull ache to severe pain and discomfort.
-
Increase the frequency of infection
Leukemia can destroy white blood cells that help fight infection. As a result, people with this condition may have a higher rate of infection and fever due to a low white blood cell count.
It seems that he is constantly sick, suffering from various viral and bacterial diseases. They can also have a crazy temperature.
-
Enlarged lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes are an important part of the body’s immune system because they filter and remove potentially harmful substances from the body. As leukemia cells spread and grow, they can reach lymph nodes throughout the body.
A person or doctor can feel a lymph node as a fluid-filled lump under the skin.
Common places where swollen lymph nodes can appear include:
- On both sides of the neck
- side of the neck
- in the hand
Sometimes the swelling of the lymph nodes does not reach the level where a person can feel the swelling.
Early symptoms of leukemia
In many cases, the initial symptoms are flu-like, but unlike flu symptoms, they do not go away.
Common early symptoms of leukemia include:
- loss of appetite
- bone pain
- easy to bite
- nervous
- the summer
- often contaminated
- Headache
- heavy bleeding
- joint pain
- night sweats
- Difficulty breathing
If your symptoms do not improve after a few weeks, see your doctor.
Symptoms of acute and chronic leukemia
Doctors can classify leukemia as acute or chronic. The onset of acute leukemia is sudden, and the cancer cells grow rapidly. Chronic disease involves slow growth of cancer cells, and symptoms may take years to appear.
However, acute leukemia and chronic leukemia have some similarities. Both can cause flu-like symptoms, fatigue and a general feeling of being sick.
Symptoms of chronic leukemia include:
- anemia
- loss of appetite
- Discomfort or bloating in the upper left side of the abdomen (where the spleen is)
- easy bleeding or bruising
- Tired easily
- Swollen lymph nodes that are not painful to the touch
- the summer
- night sweats
- lose weight
Symptoms of acute leukemia include:
- bone pain
- slow cut to remove
- Fatigue that doesn’t go away even with rest
- persistent infection
- joint pain
- low fever
- night sweats
- pale skin
- Small red spots on the skin, which doctors call petechiae
These are some of the symptoms of acute and chronic leukemia. A person may have other symptoms instead of this or in addition to it.
When to see a doctor
If you have any of the following symptoms that may be caused by leukemia, you should see your doctor:
- loss of appetite
- mild fever that does not go away
- frequent and prolonged infections
- unexplained fatigue
- unexplained weight loss
You should consult your doctor if you have other symptoms that indicate a change in your medical history that affects your health.
Causes and Risk Factors
Doctors have not identified a single underlying cause of leukemia. Instead, we believe that many factors influence a person’s likelihood of getting sick.
- the elderly
- a close relative with leukemia, such as a parent or sibling
- chemotherapy or radiation before other cancer treatments
- smoking history
- History of exposure to chemicals such as Agent Orange and benzene
- history of high levels of radiation exposure
However, having these risk factors does not mean that you will develop leukemia.
The diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose leukemia with a combination of blood tests that measure the average level of certain blood cells. Your doctor may also do a bone marrow biopsy to check for cancer cells or other harmful cells in your body.
The process
Treatment options for leukemia depend on the type of leukemia your doctor has diagnosed.
Possible treatments include:
- chemical treatment
- immunomodulator
- immunosuppressive therapy
- splenectomy, surgical removal of the spleen
- stem cell transplant
Again, the best treatment depends on the underlying cause of the leukemia.
Appearance
Survival rates for people with leukemia depend on many factors, including the type of leukemia, age at diagnosis, and when doctors diagnosed the disease.
People diagnosed with leukemia should talk to their doctor about their chances of survival and how treatment can change their outlook.
Overview
Leukemia can cause a variety of symptoms. At first, the symptoms can be confused with a viral or bacterial disease. Other blood tests may show lower-than-expected blood counts, prompting doctors to order more diagnostic tests.
If you suspect that your symptoms may be leukemia, talk to your doctor.