Health
Low and normal blood oxygen levels: What to know

Low and normal blood oxygen levels: What to know
Red blood cells carry a lot of oxygen, take it from the lungs and distribute it to all parts of the body.
The body carefully monitors blood oxygen levels to keep them within a certain range so that each cell has enough oxygen to meet its needs.
The level of oxygen in a person’s blood measures how well the body transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells and is important to a person’s health.
Normal and low blood oxygen levels
A healthy blood oxygen level is between 75 and 100 millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
If the blood gas (ABG) test shows an oxygen level of less than 60 mmHg. Artists and the medical community are trying to minimize it. In some cases, people with these findings may need supplemental oxygen.
Blood oxygen levels that are too low for the average healthy person are a sign of a condition known as hypoxia. It occurs when the body has difficulty delivering oxygen to all its cells, tissues, and organs.
Oxygen saturation
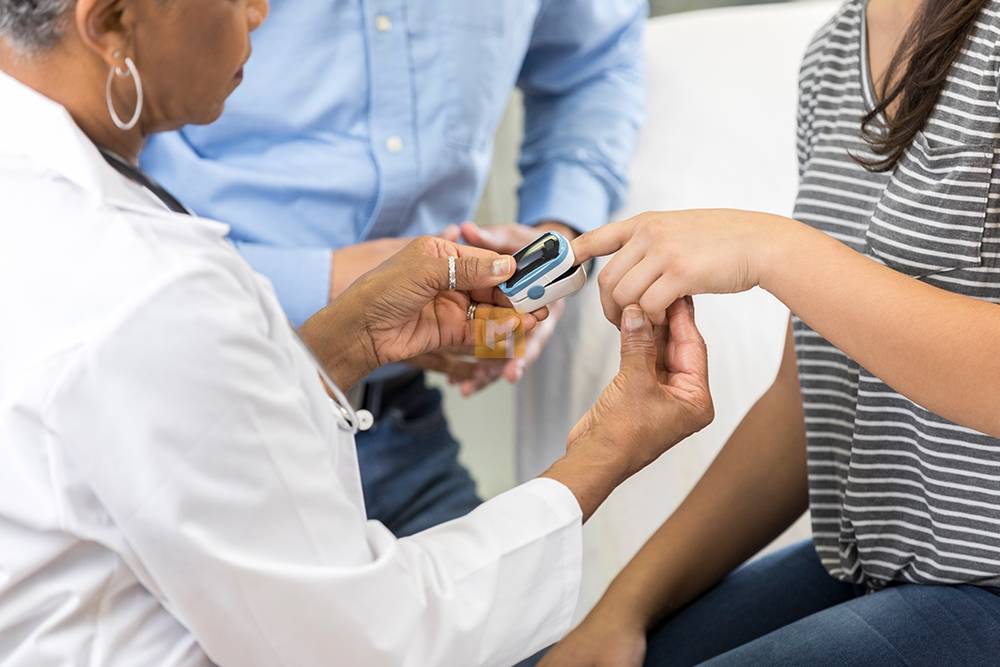
Health care professionals often use a device called a pulse oximeter for quick testing and continuous monitoring. The device can be attached to a person’s fingers.
A healthy oxygen saturation level is 95% to 100%. If a person’s levels are below this threshold, symptoms of hypoxia such as shortness of breath and confusion may occur.
How is oxygen measured in blood?
ABG testing is a common way to monitor blood oxygen levels. For this test, a blood sample is usually taken from an artery in the wrist. Although this method is very accurate, it can be quite painful.
The doctor is doing an ABG test at the hospital. However, you can test yourself at home using a small device called a pulse oximeter. ABG testing cannot be done at home.
A pulse oximeter is usually a small clip on your finger, but you can also use it on your ear or foot. It indirectly measures the oxygen content of the blood by absorbing light from a person’s pulse.
Blood oxygen testing is easier, faster and less painful than ABG testing, but it is not as accurate. Many factors can affect your results, including the credibility of the source.
- dirty fingers
- the light
- Dark skin color
- yeast
- Impaired blood circulation to the muscles
Symptoms of low blood oxygen levels
Low blood oxygen levels can reduce circulation and cause symptoms such as:
- Hold your breath
- headache
- worry
- dizziness
- rapid breathing
- chest
- confused
- high pressure
- Lack of coordination
- the blind
- anxiety
- Arrhythmic heartbeat
What causes low blood oxygen levels?
The medical term for low blood oxygen is lack of oxygen in the blood. This can cause:
Lack of oxygen in the air
The lungs do not get oxygen and deliver it to all cells and tissues
Blood does not circulate through the lungs and carries oxygen throughout the body
Conditions that cause hypoxia
Many conditions and medical conditions contribute to the above factors, including:
- asthma
- Heart disease including congenital heart disease
- plateau
- Anemia
- A reliable source of information about COVID-19
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Interstitial lung disease
- Perforated lung ventilation
- acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Pneumonia
- Obstruction of the pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary fibrosis, or scarring and damage to the lungs
- Air or gas in the chest can cause the lungs to collapse
- Excess fluid in the lungs
- Sleep apnea, including breathing disturbances during sleep
Certain medications, including certain medications and pain relievers
When to call the doctor
People should see a doctor if:
- Experience severe and sudden shortness of breath
- Shortness of breath at rest.
- Shortness of breath that worsens with exertion or physical exertion.
- Suddenly waking up with shortness of breath or feeling tired
- At altitude, he suffered from severe shortness of breath, coughing, palpitations and fluid retention.
Pay attention
Treatment options for low blood oxygen include supplemental oxygen. Doctors can prescribe in-office oxygen therapy and may also prescribe or recommend home oxygen therapy (HOT).
There are many heat tracking and delivery devices available, but some require a prescription.
People can make lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms of hypoxia and improve overall health and quality of life. Changes that may help include:
- Stop smoking
- Avoid secondhand smoke.
- Eat a nutritious diet with plenty of fruits, whole grains, lean proteins and vegetables.
- Regular exercise
Approach
Many conditions can cause low oxygen levels in the blood. Treating the underlying condition usually improves blood oxygen levels.
People with chronic lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who have COVID-19 may need regular blood oxygen monitoring.
People with hypoxia can also make lifestyle changes, such as changing their eating and exercise habits. When combined with oxygen therapy, these changes can help increase a person’s oxygen saturation level.
Essence
The oxygen level in a person’s blood indicates the amount of oxygen in the blood. On a pulse oximeter, doctors consider this level to be less than 95 percent.
Many conditions can lower blood oxygen levels, including asthma, anemia, and COVID-19.
Treatment often involves addressing the underlying cause, but sometimes doctors recommend oxygen therapy or lifestyle changes.