Health
Everything you need to know about gout
Everything you need to know about gout
Hemorrhoids are a common type of arthritis that causes severe pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. It usually affects a joint at the end of the big toe called the metatarsophalangeal joint. The main reason for this is the presence of excess uric acid in the body.
Hemorrhoids affect more than 3 million Americans and are the most common type of inflammatory arthritis in men. Although women are generally less likely to develop postmenopausal gout.
Hemorrhoid attacks can come on quickly and recur over time. This ongoing recovery can gradually damage the tissue in the inflamed area and be very painful. High blood pressure, heart disease, and obesity are risk factors for gout.
Treatment
Hyperuricemia is the main cause of gout when there is too much uric acid in the body.
Most people treat this condition with prescription medications. These medications can help treat the symptoms of a hemorrhoid attack, prevent future flare-ups, and help with kidney stones, tuberculosis, and more.
Common medications include NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and other anti-inflammatory medications. They reduce swelling and pain in gout affected areas.
It is often a reliable source of excess uric acid, overproduction of uric acid, or kidney problems that do not adequately remove the substance. Medicines can be used to reduce the production of uric acid or to increase the kidney’s ability to remove uric acid from the body.
If left untreated, an acute gout attack occurs 12 to 24 hours after its onset. If left untreated, it may heal within 1-2 weeks, but during this time he may experience great pain.
Examination and diagnosis
Diagnosing gout is often difficult because the symptoms are similar to other symptoms. Although most people who develop ringworm have hyperuricemia, this is not the case with burns. As a result, hyperuricemia does not need to be present for diagnosis.
High levels of uric acid in a person’s blood or urate crystals in joint fluid are the main diagnostic criteria for hemorrhoids.
To assess this, the rheumatologist will perform a blood test and may take fluid from the affected joint for analysis.
Additionally, they may use ultrasound to look for urate crystals around or growing in the joints. X-rays cannot detect hemorrhoids, but healthcare professionals can use them to rule out other causes.
Because a joint infection can also cause gout symptoms, doctors may look for bacteria when examining the joint fluid to determine a bacterial cause.
Types
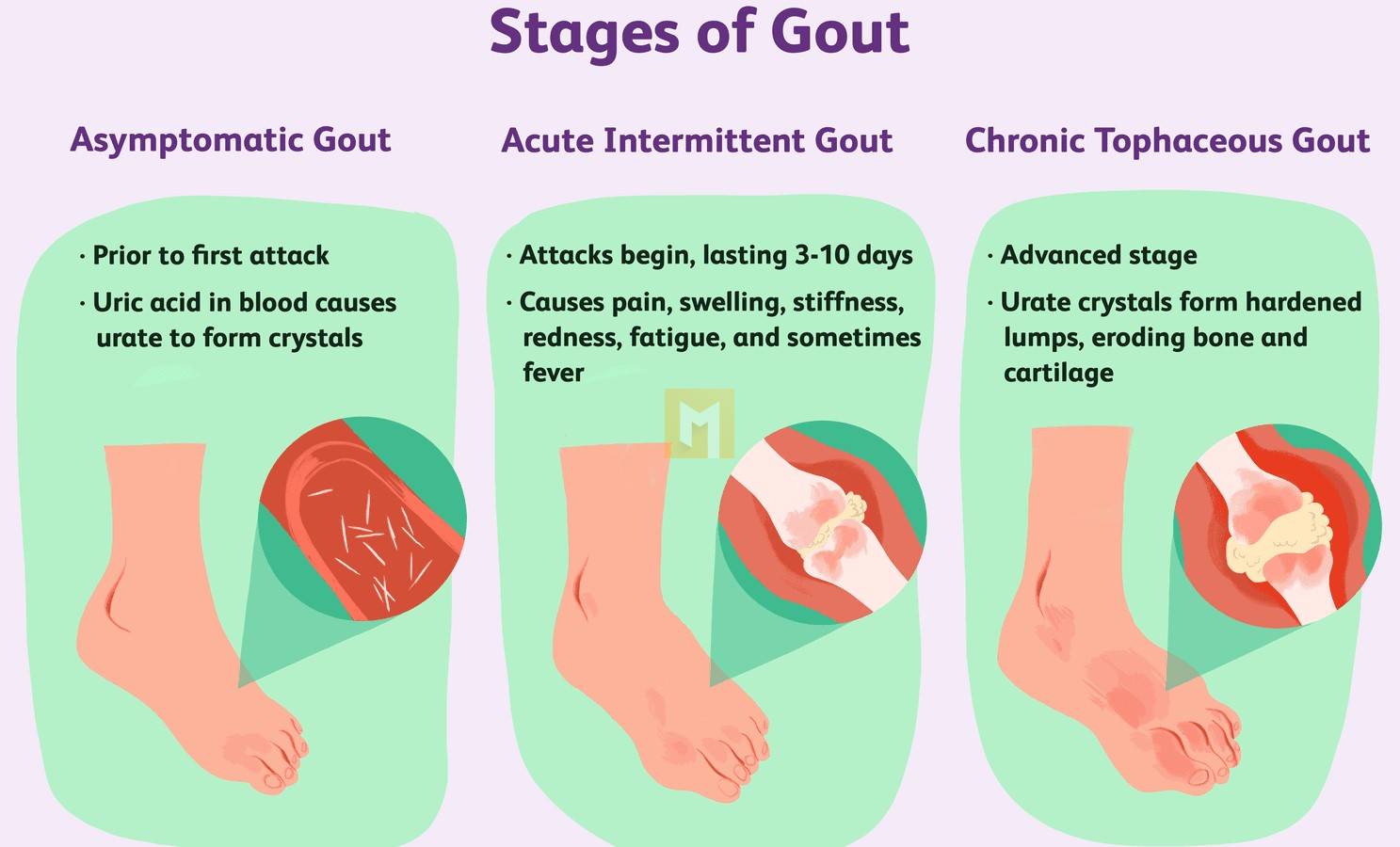
There are different stages in the development of gout.
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Uric acid levels can rise without any outward symptoms. Although people at this stage do not need treatment, high levels of uric acid in the blood can cause silent tissue damage from a reliable source.
As a result, a doctor may recommend that a person with high uric acid levels address factors that may contribute to its formation.
Acute hemorrhoids
This condition occurs when urate crystals in the joints spontaneously cause severe inflammation and severe pain. This sudden attack is a “cure” and can last from 3 days to 2 weeks. Stressful life events and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to burnout.
Intermediate or interstitial hemorrhoids
This stage is the time between serious finger injuries. As a person’s fingers grow, these spots become smaller. During this period, urate crystals may accumulate in the tissue.
Joints
Chronic nodular gout is the most debilitating form of gout and can cause permanent bone and kidney damage. During this time, arthritis sets in and tophi can form in cold areas of the body, such as the fingers.
Gout often develops after many years and is a sure source of gout.
Pseudogout
A condition that experts often confuse with gout is calcium pyrophosphate deposits called pseudogout. The symptoms of pseudogout are similar to those of gout, but the inflammation is usually less severe.
The main difference between gout and pseudogout is that the bones are inflamed with calcium pyrophosphate crystals instead of urate crystals. Pseudogout requires different treatment than gout.
Reason
Hyperuricemia is an excess of uric acid in the blood and is the main cause of gout.
The body produces uric acid during the breakdown of purine compounds. These are chemicals found in other foods such as meat, poultry and seafood.
Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is excreted from the body through the kidneys in the form of urine. If too much uric acid is produced or not enough is excreted, uric acid can build up and form needle-like crystals. This causes inflammation and pain in the surrounding joints and muscles.
Danger
There are several factors that can increase the risk of hyperuricemia and gout:
Age: Gout is more common in the elderly and rarely affects children.
Sex: In people under 65, arthritis is four times more common in men than in women. It falls a little more than three times over the age of 65.
Genetics: having a family history of gout increases the chances of developing gout.
Lifestyle choices: Alcohol consumption interferes with the excretion of uric acid from the body. Eating foods rich in purines also increases the amount of uric acid in the body. All of these can cause gout.
Looking ahead: Research shows a link between chronic exposure and an increased risk of arthritis.
Medicines: Some medicines can increase the amount of uric acid in the body. These include diuretics and products containing salicylic acid.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese and having excess abdominal fat increases the risk of gout. However, being overweight or obese is not a direct cause.
Other Diseases: Kidney failure and other kidney diseases reduce the body’s ability to eliminate waste and increase uric acid. Other diseases associated with gout are high blood pressure and diabetes.
Mark
The main symptom of gout is severe pain, which ends with discomfort, swelling and redness.
The condition usually affects the underside of the big toe, but can also occur in the forearm, ankle, knee, elbow, wrist and fingers.
Problems
In some cases, gout can be more serious, such as kidney stones or gout.
Prevention tips
There are many lifestyle strategies and diets you can try to prevent inflammation or prevent gout.
- Try to drink plenty of water, about 2-4 liters a day
- Avoid alcohol.
- Continue to gain weight
Homemade medicine
People with gout can control flare-ups by controlling what they eat and drink – a balanced diet can help reduce symptoms.
An important first step is to cut back on purine-rich foods and beverages so your blood uric acid levels don’t rise too high.
Purine-rich foods:
- Red meat
- meat game
- Glandular meats such as kidneys, liver and sweet breads
- Seafood
- the shell
- alcohol
People can reduce their risk of developing gout by limiting their intake of purine-rich foods. However, there is no need to avoid purine consumption. Moderate consumption of purine-rich foods helps regulate uric acid levels and benefits gout symptoms and overall nutritional health.
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis. As a result, people with gout symptoms can benefit from simple arthritis treatments at home. This includes staying involved, maintaining a moderate weight, and low-impact exercise to support joint health.
Summary
Gout is a common form of arthritis that affects the joints. The condition affects more than 3 million Americans and is more common in men than women.
Hyperuricemia – when a person has too much uric acid in the blood – is the main cause of gout.
People can develop hyperuricemia if the body produces too much uric acid or if the kidneys do not excrete it properly.
Doctors often prescribe medications to treat gout. This may include treatment to reduce inflammation in the affected joint and medications to control uric acid levels.
People can help reduce their risk of developing gout by avoiding foods high in purines, which the body converts to uric acid, staying adequately hydrated, and avoiding alcohol.